What is cancer? Cancer is a disease characterized by the presence of malignant tumors in the body. Malignant tumors can spread into surrounding tissues and invade other parts of the body displacing normal tissue and interrupting organ function as it grows. A tumor grows from a single cancer cell. It starts when the cell undergoes transformation, converting a normal cell to a cancer cell. A transformed cell grows abnormally and the immune system usually recognizes it and destroys it. If the cell somehow avoids destruction, it may multiply to form a tumor. A tumor is a mass of abnormally growing cells with otherwise normal tissue. If the abnormal cells remain in their original spot, then a benign tumor has formed. These tumors can be dangerous if they spread to the brain but if they maintain size and location they can be left alone. If needed, they can be completely surgically removed. What you don't want is for the cancer cells to spread through lymph and blood vessels to other parts of the body. This process is called metastasis. Unfortunately, cancer cells are not density-dependent. If they were, they would stop multiplying when they have filled a single layer. Instead they keep dividing, forming a clump of overlapping cells.
http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-bLMsNN3xWmA/UDV2oRDnB3I/AAAAAAAAJDY/vTXEmUk0mKA/s640/The+growth+of+breast+cancer.jpg
Sunday, September 21, 2014
Down Syndrome
An extra copy of chromosome 21 is what causes down syndrome. In a normal human complement, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes. But what is down syndrome and what causes this to happen? Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which a person has 47 chromosomes instead of 46, which is the normal amount. This is also a related to trisomy 21. Trisomy 21 is when there are three number 21 chromosomes, making 47 chromosomes in total. It is the most common chromosome number abnormality and the most common serious birth defect in the U.S. It affects about one out of every seven hundred children. Some of the characteristics of a person with down syndrome possess a round face, a skin fold at the inner corner of the eye, a flattened nose bridge, and small, irregular teeth. They're also short and have heart defects. As well as susceptibility to respiratory infections, leukemia, and Alzheimer's disease. Generally, people with down syndrome have a shorter life span than others. The older a woman is when she has a baby, the higher the percentage is for her to have a child with this chromosome defect. Less than .05% in women under the age of 30, 1% for mothers at age 40, and the percentage is even higher for older mothers.
http://anthro.palomar.edu/abnormal/images/Down_Syndrome_Karyotype.jpg
http://anthro.palomar.edu/abnormal/images/Down_Syndrome_Karyotype.jpg
Thursday, September 18, 2014
Chemical Cycling and Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Did you know that we as humans inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide? And did you know that plants and most other organisms do the exact same thing? But how? The ecosystem works in an amazing way. The sun is the light energy for the entire ecosystem. It keeps the plants growing, which are the producers for the ecosystem. Trees absorb water and minerals through its roots from the soil and its leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air. The leaves then release oxygen into the air. The consumers of the ecosystem are the animals. They eat the plants and other animals. Decomposers such as, worms, fungi, and bacteria return chemicals back to the soil by changing complex matter into simpler chemicals. The most basic chemicals necessary for life are carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, and various minerals. As you can see, the ecosystem is a big, never ending cycle of producers and consumers. Nothing can do anything without the step before it and after it.
Saturday, September 13, 2014
Alcoholic Fermentation
Alcoholic fermentation is one of two pathways, lactic fermentation being the other. Both fermentations occur in two stages. In the first stage, yeast breaks down glucose into pyruvate through a process called glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first stage in cellular respiration in all organisms. It is a process that cells use to break down glucose for energy. Pyruvate is what happens as a result of glycolysis. A carbon dioxide molecule is removed from the pyruvic acid leaving a two-carbon compound. In the second stage, two hydrogen atoms from NADH and N+ are combined to the two-carbon compound to create ethyl alcohol. The NADH is oxidized to make NAD+. Oxidation is when a substance loses electrons. NADH is the reduced state of NAD+.
- In Biology 101, we took 1 tablespoon of sugar and a small packet of yeast and mixed them together in warm water. Next we put it inside a 20oz plastic bottle and tightly covered the top of the bottle with a rubber glove and let it sit for about 20 minutes. The glove started to expand from the carbon dioxide being released. This process is used to create wine, beer, and bread. This example is a representation of alcoholic fermentation.
Biology
Biology is an interesting subject. It's one of its own in many ways. It tells you how the whole world; from the air we breathe to the germs on our counters; is made up of molecules and cells that you can't see with the naked eye. Many scientists have dedicated their lives to discovering things and how they work. In November of 1859, Charles Darwin wrote a book called On The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection which was about evolution. Evolution is the process that explains how life on Earth was billions of years ago in relation to now. Peter Agre was another scientist. He made the discovery of aquaporins. This discovery lead him and his partner, Roderick MacKinnon, to get the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2003. An aquaporin is a transport protein in the cell membrane that allows water to pass through to the membrane. These scientists, and every other scientist, has to be very open minded about things and expect anything to happen.


http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2e/Charles_Darwin_seated_crop.jpg
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8d/Peter_Agre.jpg
http://nihrecord.nih.gov/newsletters/2004/10_12_2004/images/STETLECT.jpg


http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2e/Charles_Darwin_seated_crop.jpg
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8d/Peter_Agre.jpg
http://nihrecord.nih.gov/newsletters/2004/10_12_2004/images/STETLECT.jpg
Sunday, September 7, 2014
Eukaryotic Cells
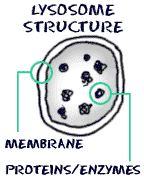
Between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells are my favorite. They're more interesting than prokaryotic cells. They contain more parts to their cells and are larger. Lysosomes and centrosomes are the only organelles that are found in eukaryotic cells that are not found in prokaryotic cells. Lysosomes are recyclers for the cells. They also work to make cells renew themselves. They are made by rough endoplasmic reticulum and work through the Golgi apparatus. Protists take in food particles into food vacuoles which digests the food. Lysosomes connect with food vacuoles and digest the food. Then nutrients are released into the cytosol. Our white blood cells take in bacteria and then get rid of them using lysosomes. A lysosome connects with enclosed damaged organelles or small amounts of cytosol located in membrane sacs and destroys its contents. As a result, it makes organic molecules available for reuse. Diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Gaucher disease are two examples from lysosome storage deficiencies.


Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




